Diseases associated with Dementia
- Neurodegenerative diseases. Neurodegenerative diseases are diseases where a gradual, often slow breakdown of the brain and its functions occurs. For example, Alzheimer’s disease, Frontotemporal dementia or Lewy body dementia.
- Vascular dementia. Vascular dementia is dementia caused by disturbances in the brain’s blood supply or blood vessel. The disturbances may be due to blood clots, bleeding or narrowing of the blood vessels of the brain.
- Other diseases. A number of other diseases with direct or indirect influence on brain function can cause cognitive impairment. For example, there may be metabolic disorders, chronic deficiency of B vitamins or poisoning conditions
The distribution of the different categories of illnesses in Denmark:
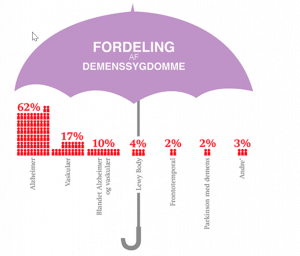 The figure shows the distribution of different diseases causing dementia in Denmark: 62% has Alzheimer’s disease, 17% has vascular dementia, 10% a mix of Alzheimer and vascular dementia, 4% has Lewy Body dementia, 2% has frontotemporal dementia, 2% has Parkinsons with dementia and other diseases cause 3%.
The figure shows the distribution of different diseases causing dementia in Denmark: 62% has Alzheimer’s disease, 17% has vascular dementia, 10% a mix of Alzheimer and vascular dementia, 4% has Lewy Body dementia, 2% has frontotemporal dementia, 2% has Parkinsons with dementia and other diseases cause 3%.
The disease process depends on the cause of the disease. Most dementia diseases are progressive disorders that cannot be cured. The course may vary from a year to several decades.
Dementia diseases are generally not hereditary. In Alzheimer’s disease, only 2-3% of the cases are directly due to inheritance. The reason for the other cases of Alzheimer’s is more uncertain.
Frontotemporal dementia is the common name for a group of relatively rare diseases, which account for only 5-10% of the total number of dementia. Frontotemporal dementia is more commonly inherited, as up to 40% of the cases are genetically conditioned.
The possibility of treatment is different, depending on which disease is the basic one. Counseling and practical assistance, care and relieving of relatives are important elements of the treatment. In addition, doctors since the 1990’s have been able to prescribe medications that temporarily reduce the symptoms of, for example, Alzheimer’s disease. In vascular dementia, which may be due to blood clots in the brain, the treatment aims to prevent the formation of more blood clots. Some of the diseases can be cured, eg, metabolic disorders, depression, side effects or misuse of medicines. Therefore, it is important to clarify the cause of the symptoms and diagnose as early as possible.
